MCP Gateway
User guide
Connect to MCP servers your organization has approved.
Find available servers
- Log in to MintMCP
- Click MCP store in the sidebar
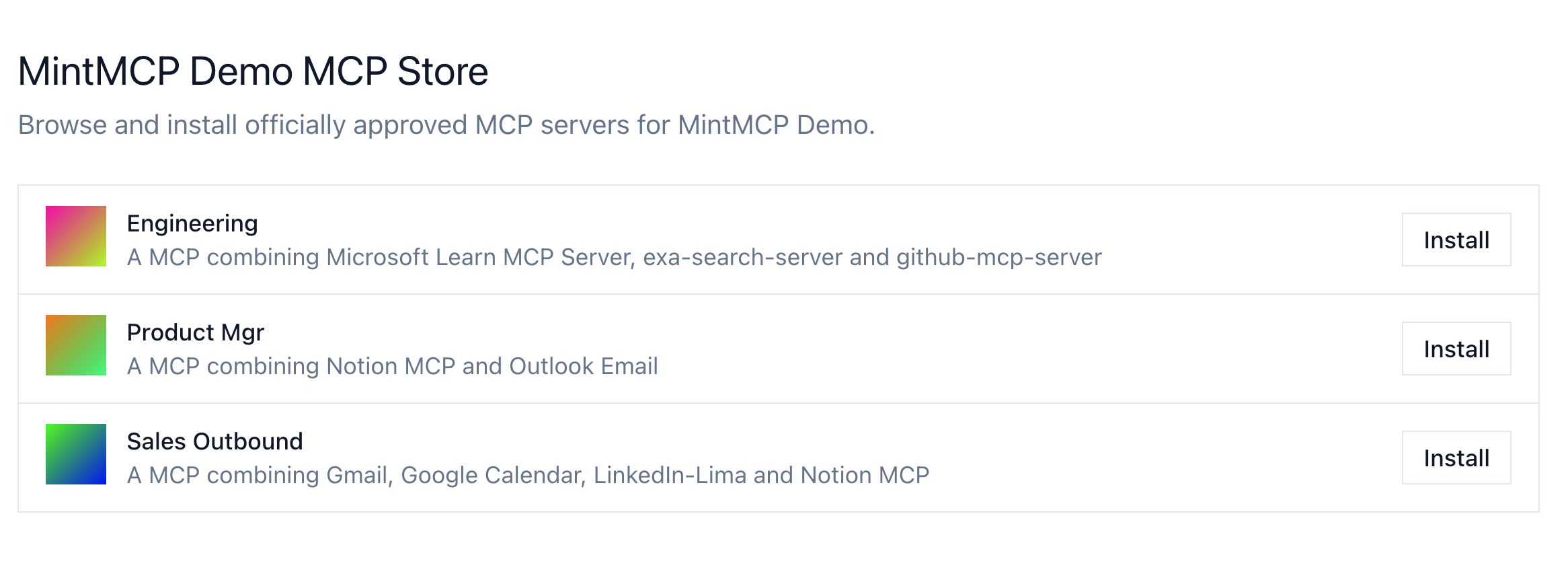
The store shows MCP servers your administrator has approved. Each entry displays:
- Server name and description
- Which connectors are included
- An Install button to get connection instructions
Installing an MCP server
Click Install on any MCP server to see setup instructions for your AI client.
ChatGPT setup
For ChatGPT Custom GPTs, you'll need:
- The MCP server URL
- Authentication credentials (API key or OAuth configuration)
Follow the on-screen instructions to add the server as a Custom Action in your GPT.
Claude and other MCP clients
For clients with native MCP support:
- Copy the MCP server URL from the install dialog
- Add it to your client's MCP configuration
- Authenticate when prompted
Authentication
First-time connection
When you first connect to an MCP server:
- Your AI client initiates the connection
- MintMCP prompts you to sign in (using your organization's SSO if configured)
- MintMCP validates your permissions
- You can start using the tools
This happens once per MCP server. Your credentials are cached for future sessions.
Per-user authentication
Some MCP connectors require you to authenticate with the underlying service. For example, a GitHub connector might need your personal GitHub authorization.
When this happens:
- Your AI agent calls a tool that needs your credentials
- The client displays an authentication link
- Click the link and authorize access to the service
- MintMCP stores your authorization for future requests
Troubleshooting
Can't see any MCP servers
- Verify you're logged into MintMCP with your work account
- Check that you're in the correct organization (see bottom-left of sidebar)
- Contact your administrator to request access
Authentication fails
- Make sure you're using your organization credentials
- If using SSO, ensure your SSO session is active
- Clear your browser cache and try again
Tools not working
- Check if the connector requires per-user authentication
- Verify the underlying service (GitHub, Slack, etc.) is accessible
- Contact your administrator if the issue persists
Next steps
- Ask your administrator about MCP servers available for your role
- Core concepts — How MCP servers work